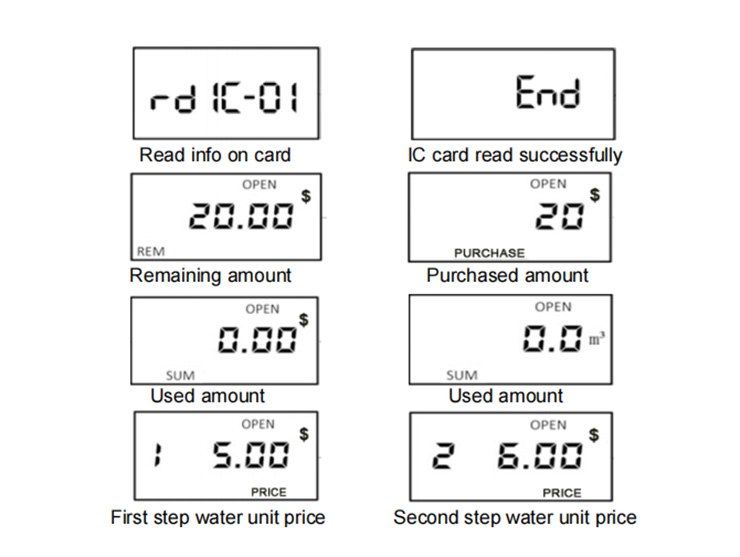
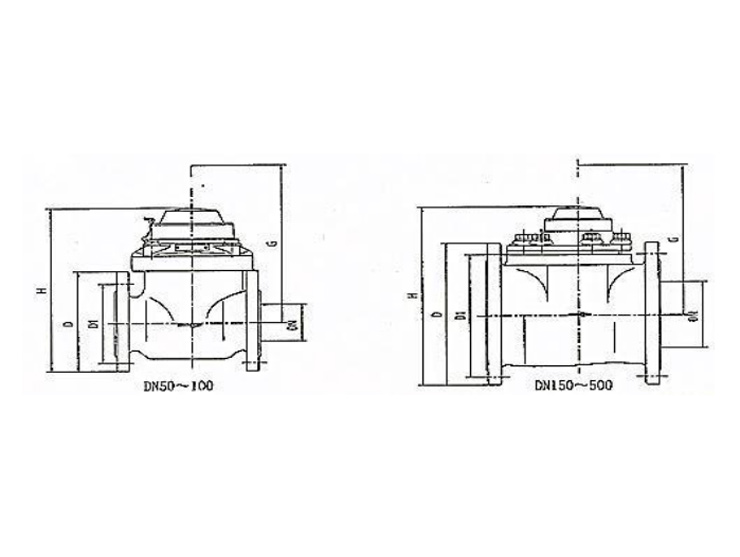
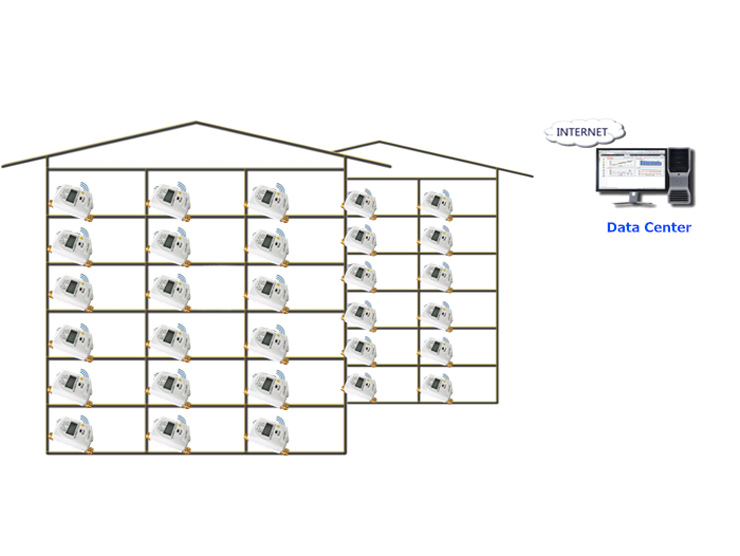
News
Do you know the difference between solenoid valves and electric valves?
The difference between solenoid valve and electric valve
1. Switching form:
The solenoid valve is driven by a coil and can only be opened or closed. The switching time is very short.
The drive of the electric valve is usually driven by an electric motor. It takes a certain amount of time to simulate an open or close action and can be adjusted.
2. Nature of work:
Solenoid valves typically have a small flow coefficient and a small operating pressure differential. For example, a typical 25-caliber solenoid valve has a smaller flow coefficient than a 15-caliber electric ball valve. The solenoid valve is driven by a solenoid and is relatively susceptible to damage from voltage surges. It is equivalent to the function of the switch and is the function of opening and closing.
The drive of the electric valve is usually an electric motor, which is more resistant to voltage shocks. The solenoid valve opens quickly and closes quickly. It is typically used for small flows and small pressures, and requires electrical switching where the switching frequency is high. The opening of the electric valve can be controlled. The state has on, off, half open and a half off, which can control the flow of the medium in the pipeline, and the solenoid valve cannot meet this requirement.
Solenoid valves are suitable for certain special process requirements, such as leaks, special fluid media, etc. It is more expensive.
Motorized valves are typically used for adjustment and have a switching amount, for example: fan coil end.
The electromagnetic coil magnetically attracts the solenoid valve, and the valve core is driven against the spring pressure. The electromagnetic coil has a simple structure and a low price, and can only realize the switch.
The electric valve drives the valve core through a motor driven valve stem, and the electric valve is divided into a (stop valve) and a regulating valve. The shutoff valve is a two-position operation that is fully open and fully closed. The regulating valve is equipped with an electric valve positioner on the top, and the valve is dynamically stabilized in one position by closed loop adjustment.
Using electric and solenoid valves
Solenoid valve: The switching control of liquid and gas lines is dual DO control. Generally used to control small pipes.
Motorized valves: Analog adjustment of pipe media flow in liquid, gas and wind systems, is AI control. In the control of large valves and wind systems, electric valves can also be used for two-position switch control.
1. Switching form:
The solenoid valve is driven by a coil and can only be opened or closed. The switching time is very short.
The drive of the electric valve is usually driven by an electric motor. It takes a certain amount of time to simulate an open or close action and can be adjusted.
2. Nature of work:
Solenoid valves typically have a small flow coefficient and a small operating pressure differential. For example, a typical 25-caliber solenoid valve has a smaller flow coefficient than a 15-caliber electric ball valve. The solenoid valve is driven by a solenoid and is relatively susceptible to damage from voltage surges. It is equivalent to the function of the switch and is the function of opening and closing.
The drive of the electric valve is usually an electric motor, which is more resistant to voltage shocks. The solenoid valve opens quickly and closes quickly. It is typically used for small flows and small pressures, and requires electrical switching where the switching frequency is high. The opening of the electric valve can be controlled. The state has an on, off, half open and a half off, which can control the flow of the medium in the pipeline, and the solenoid valve cannot meet this requirement.