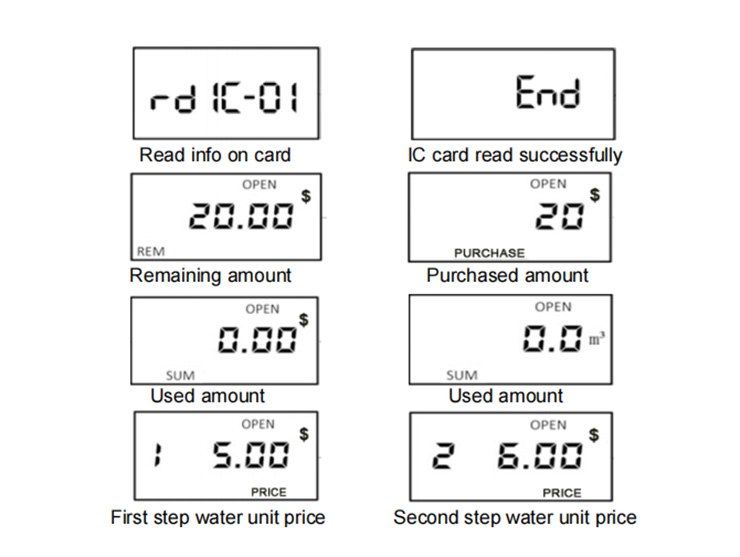
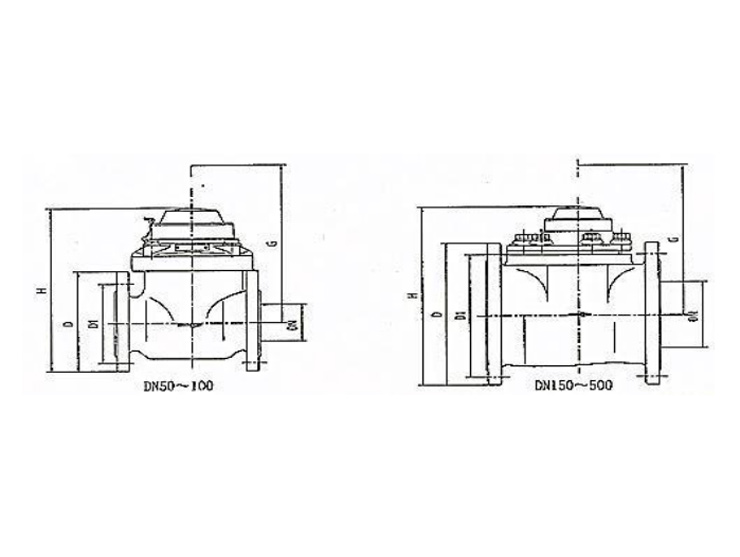
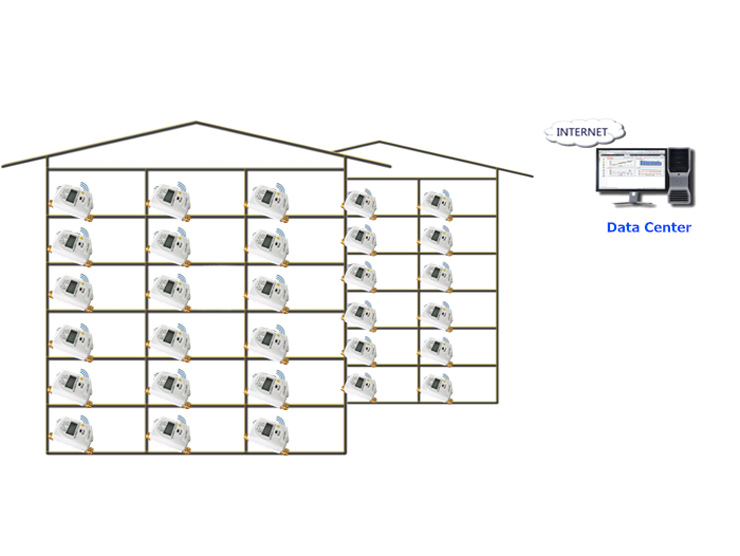
News
Brief description of the composition and properties of ductile iron
Pig iron is a carbon-carbon alloy with a carbon content greater than 2%. Industrial pig iron generally has a carbon content of 2.5% to 4% and contains elements such as C, SI, Mn, S, and P. A product smelts iron ore through a blast furnace. . According to the different forms of carbon in pig iron, it can be divided into steel pig iron, cast iron pig iron and ductile iron.
The precipitated graphite is a spherical cast iron. The splitting effect of spheroidal graphite on the metal matrix is smaller than that of flake graphite. Therefore, the strength of cast iron reaches 70-90% of the strength of the matrix structure, the tensile strength can reach 120kgf / mm 2, and the toughness is good. The chemical composition of ductile iron other than iron usually has a carbon content of 3.6 to 3.8%, a silicon content of 2.0 to 3.0%, a total amount of manganese, phosphorus and sulfur of not more than 1.5%, and an appropriate amount of a spheroidizing agent such as rare earth or magnesium.
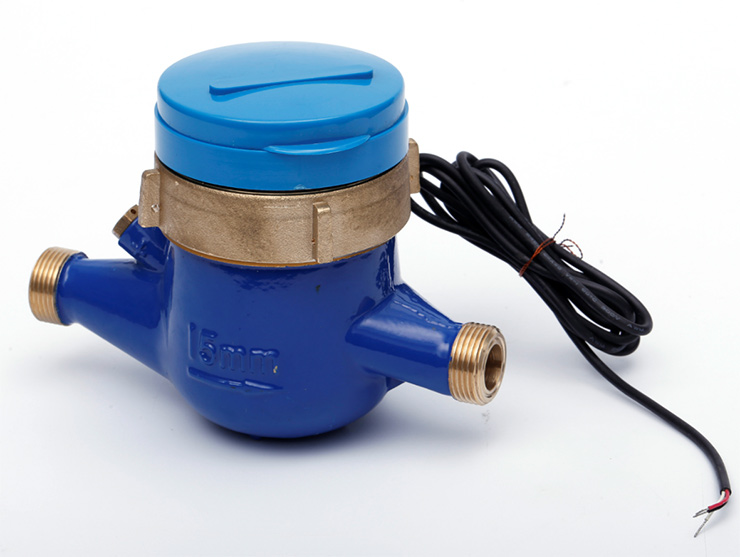
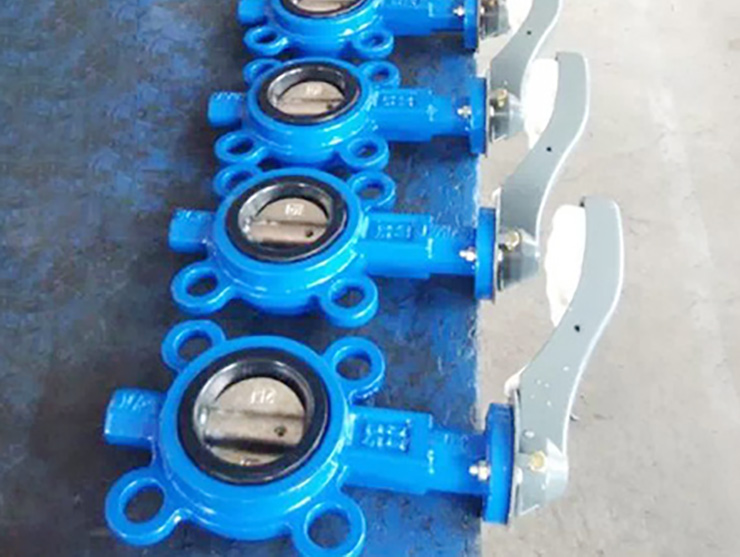
Ductile iron castings are used in almost all major industrial sectors. These components require high strength, ductility, toughness; wear resistance, stringent heat and mechanical shock resistance, high temperature or low temperature resistance as well as corrosion resistance, and dimensional stability. To meet these variations in use conditions, many grades of ductile iron are available to provide a wide range of mechanical and physical properties.
According to ISO 1083, most ductile iron castings are mainly produced in a non-alloy state. Obviously, the series includes high strength grades with tensile strengths greater than 800 Newton/mm and elongations of 2%. At the other extreme is a high resistance grade with an elongation of over 17% and a corresponding low strength minimum of 370 N / m spoon. Strength and elongation are not the only basis for the designer to select materials, while other critically important properties include yield strength, modulus of elasticity, wear and fatigue strength, hardness and impact properties. In addition, corrosion resistance, oxidation resistance and electromagnetic properties may be critical to the designer. In order to meet these special uses, austenitic ductile iron, commonly known as Ni-Resis, is invented. These austenitic ductile irons are mainly alloyed with zinc, chromium and manganese and are included in international standards.
The precipitated graphite is a spherical cast iron. The splitting effect of spheroidal graphite on the metal matrix is smaller than that of flake graphite. Therefore, the strength of cast iron reaches 70-90% of the strength of the matrix structure, the tensile strength can reach 120kgf / mm 2, and the toughness is good. The chemical composition of ductile iron other than iron usually has a carbon content of 3.6 to 3.8%, a silicon content of 2.0 to 3.0%, a total amount of manganese, phosphorus and sulfur of not more than 1.5%, and an appropriate amount of a spheroidizing agent such as rare earth or magnesium.
Ductile iron castings are used in almost all major industrial sectors. These components require high strength, ductility, toughness; wear resistance, stringent heat and mechanical shock resistance, high temperature or low temperature resistance as well as corrosion resistance, and dimensional stability. To meet these variations in use conditions, many grades of ductile iron are available to provide a wide range of mechanical and physical properties.
According to ISO 1083, most ductile iron castings are mainly produced in a non-alloy state. Obviously, the series includes high strength grades with tensile strengths greater than 800 Newton/mm and elongations of 2%. At the other extreme is a high resistance grade with an elongation of over 17% and a corresponding low strength minimum of 370 N / m spoon. Strength and elongation are not the only basis for the designer to select materials, while other critically important properties include yield strength, modulus of elasticity, wear and fatigue strength, hardness and impact properties. In addition, corrosion resistance, oxidation resistance and electromagnetic properties may be critical to the designer. In order to meet these special uses, austenitic ductile iron, commonly known as Ni-Resis, is invented. These austenitic ductile irons are mainly alloyed with zinc, chromium and manganese and are included in international standards.